Isometric Drawings
Category
Design
Date
26.08.2025
Author
Eneca
Share
Isometric drawing is a type of technical drawing that represents piping in an axonometric projection, normally in an isometric projection. It displays piping in a three-dimensional view while maintaining proportions and angles, which simplifies understanding of spatial arrangement and installation.
Isometric piping drawings are used for design, fabrication, and installation of piping systems. They provide complete information about the layout of pipes, valves, supports, welds, and other pipeline components, as well as necessary dimensions for installation.
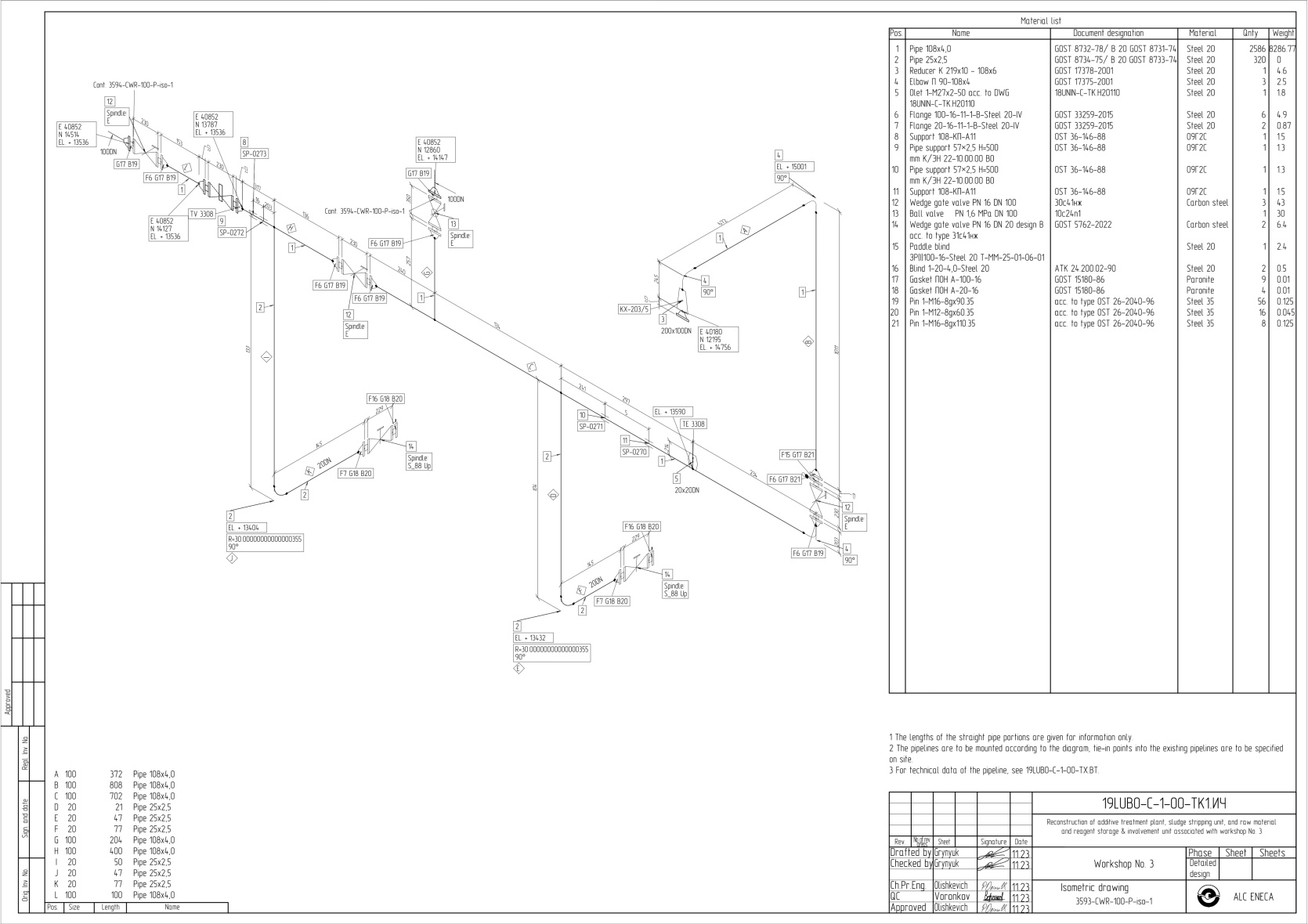
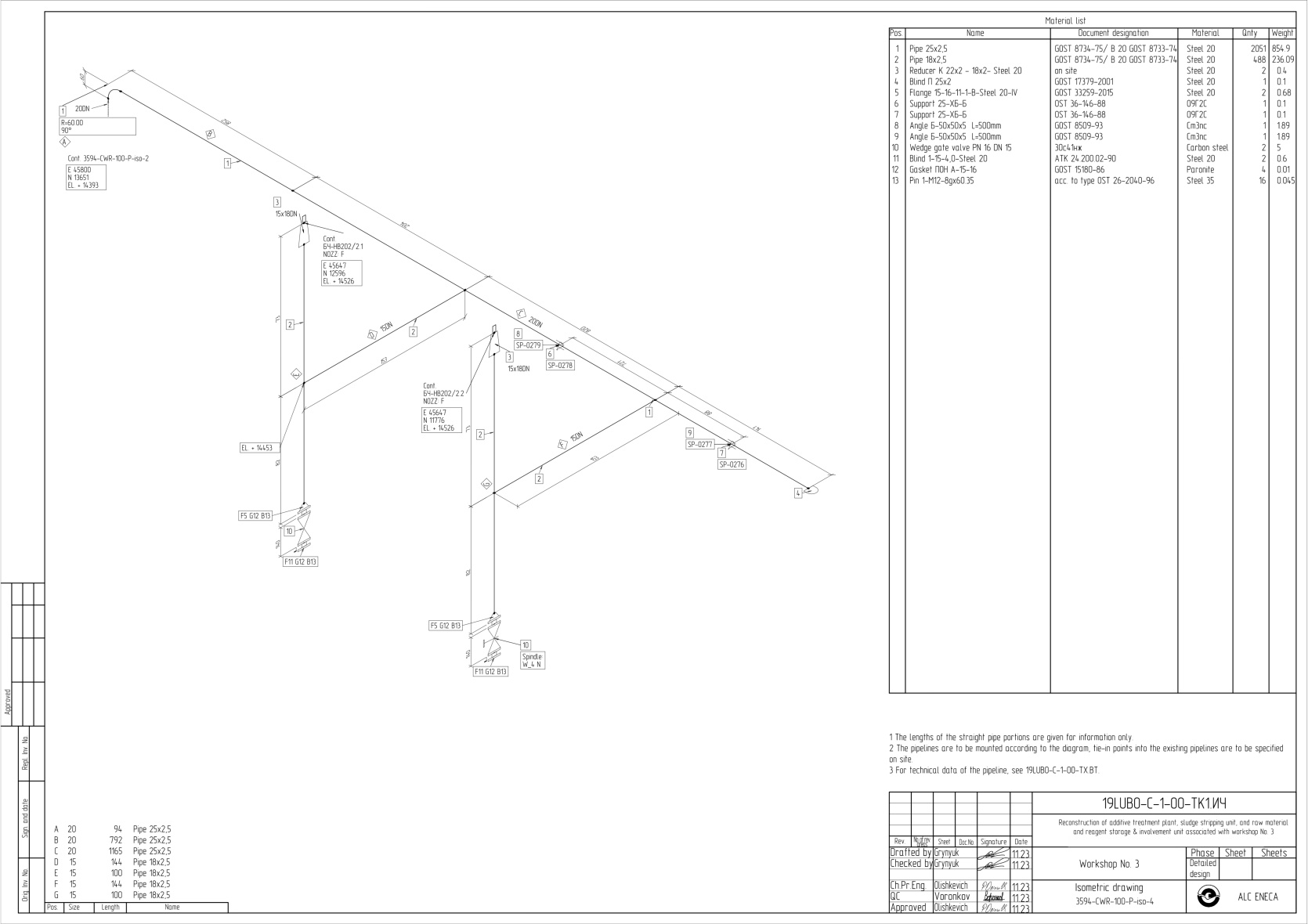
Design discipline “Process & piping engineering” is a starting point for designing adjacent design disciplines of the project: electrical supply, water supply and sanitation, ventilation, and other utility systems involved in the technological process.
Isometric piping drawings are used for design, fabrication, and installation of piping systems. They provide complete information about the layout of pipes, valves, supports, welds, and other pipeline components, as well as necessary dimensions for installation.

Drawing Elements:
Isometric piping drawings include:- Graphical symbols for piping, valves, equipment, and other components
- Dimensions required for installation (lengths, angles, coordinates)
- Component positions corresponding to the list
- Instructions for insulation, welds, supports, and other critical elements
- Reference dimensions and elevation marks.
- Instructions for structural collisions

Installation importance:
Isometric drawings are critically important for proper piping installation. They help avoid errors during pipe routing, especially in complex areas, and ensure correct connection of all components.Insulation:
Isometric drawings may include piping sections requiring insulation using dashed lines that show the necessary clearance for insulation material.Design discipline “Process & piping engineering” is a starting point for designing adjacent design disciplines of the project: electrical supply, water supply and sanitation, ventilation, and other utility systems involved in the technological process.